Network setup
We recommend setting up a static IP address for each SaunaFS server.
SaunaFS SAN (Storage Area Network) is a single IP access private network. This refers to the fact that there is only one floating IP address that clients use to access the SAN. Floating in this case means, this IP address can be assigned to different servers, which helps to improve performance and reliability.
Client connection to SaunaFS SAN
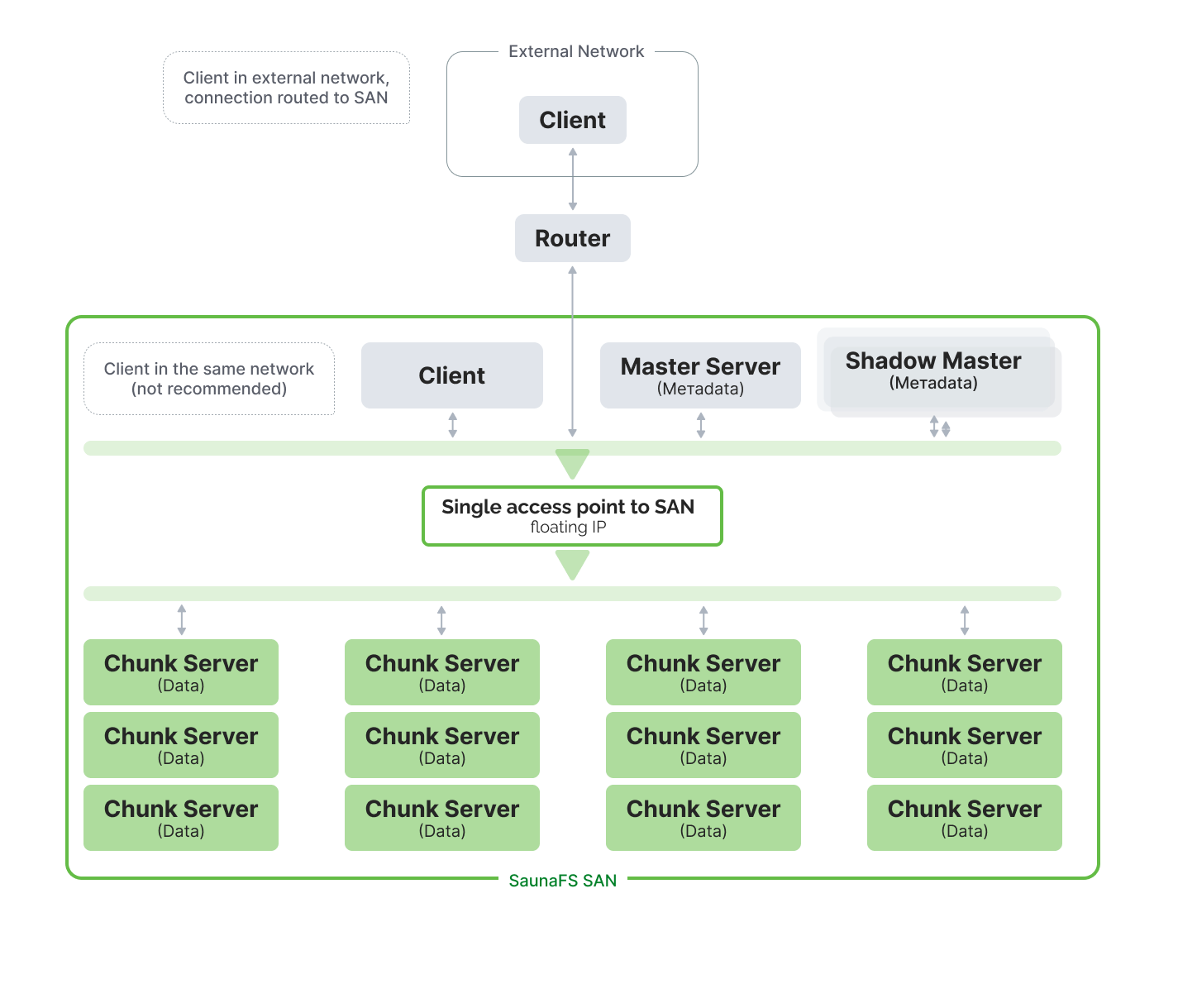
In general, there are two ways for a client to connect to SaunaFS SAN (both illustrated in the according diagram):
- Client is in external network (outside SaunaFS’s storage system's private network). In that case connection can be routed to SAN with VPN or physical router device.
- Client is in the same network. Client computer is located within the same network as the SaunaFS storage system. However, this is not recommended for security reasons.
DNS
We do not recommend using DNS to resolve the IP addresses of the system. If something in the DNS breaks, it could cause some critical services to not work properly.
Instead, assign the IP addresses a name in /etc/hosts.
Network Topology
The configuration of rack awareness in a SaunaFS network involves setting up the network topology in the sfstopology.cfg file. This file specifies the topology using lines that include an ADDRESS and a SWITCH-NUMBER. ADDRESS can be defined in various ways, including as a wildcard for all addresses, a single IP address, an IP class with a network address and bits number or mask, or an IP range.
| * | all addresses |
| n.n.n.n | single IP address |
| n.n.n.n/b | IP class specified by network address and bits number |
| n.n.n.n/m.m.m.m | IP class specified by network address and mask |
| f.f.f.f-t.t.t.t | IP range specified by from-to addresses (inclusive) |
The switch number is a positive 32-bit integer. The distances calculated from this configuration are used to prioritize chunk servers during read/write operations based on their proximity to a client. Servers closer to a client are preferred.
However, new chunks are still created randomly to ensure equal distribution, and rebalancing procedures do not consider topology configuration. The distance between switches is categorized as 0 (same IP addresses), 1 (different IP addresses but same switch number), or 2 (different switch numbers).
This topology feature can be effectively combined with chunk server labeling to optimize client interactions with chunk servers, ensuring they read from or write to servers that are best suited for them, like those on the same network switch.